.
-->General information about the trial
- Serology
- Lung scoring at the slaughter house
-->Result
-->Conclusion
.
COGLAPIX® - ECONOMIC BENEFIT STUDY VERSUS AN ANTIBIOTIC IN THE CONTROL OF A.P
(Pleuropneumonia due to Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, or APP)
By PHẠM Châu Giang, Swine Technical Rep. - CEVA Animal Health Vietnam
.
WHY HAVE TO CONTROL A.P.?
A.p. (Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, or APP) is a Gram negative bacterium, usually cause the illness and death in fattening pigs. Infected pigs have dyspnea, abdominal breathing, the mortality is high in case of outbreak. The dead usually happen with blood exudate from the nose, abcessus and necrosis of the lung.
Image 1Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae
The loss due to A.p. is very high. The mortality can reach 15% in an outbreak (R. Krejci, 2010). In chronical case, the ADG (average daily gain) is reduced 84g, FCR (feed conversion ratio) is increased, the slaughter day can be prolonged 6 days more (Rohrbach, 1993).
Image 2 Dead pig due to A.p.
.
GENERAL INFORMATION ABOUT THE TRIAL
The trial was done in a 3.000-sows farrow-to-finish farm by Prof. Trần Thị Dân and colleagues, Nông Lâm University, Hochiminh city, from December 2010 to May 2011. This farm has been experienced outbreaks of A.p. and the chronic situation is happen in time of trial.
The objective of this trial: to compare the economical benefit, in a weaning to finish operation contaminated by A.p., of the vaccination with COGLAPIX® versus two groups without vaccination (one using a specific antibiotic prevention against A.p., the other one not).
Image 3 Vaccine Coglapix®
This trial was presented in IPVS in May 2012, Jeju, Korea.
^ Top page
.
MATERIAL AND METHOD
BEFORE THE TRIAL
Serology
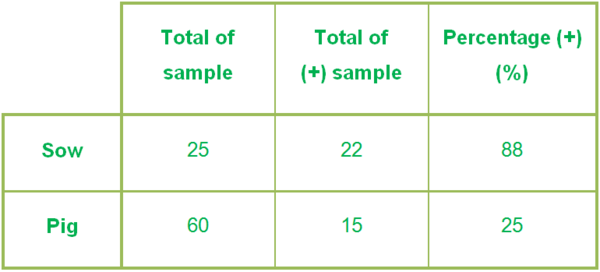
The serum samples of 25 sows and 60 pigs were collected. The method used in the trial is ELISA (ELISA ID Vet@ APP screening 1-12).
Table 1 Results of serology
The result in Table 1 showed that a percentage of positive antibody against A.p. is high. This farm didn’t use any A.p. vaccine prior to the trial, so the antibody is derived from the A.p. in the field. For this reason, we could conlude that A.p. is present in this farm.
^ Top page
.
Lung scoring at the slaughter house
Image 4 Lung scoring at the slaughter house
92 lungs of slaughtered pigs are randomly chosen to evaluate at the slaughter house.
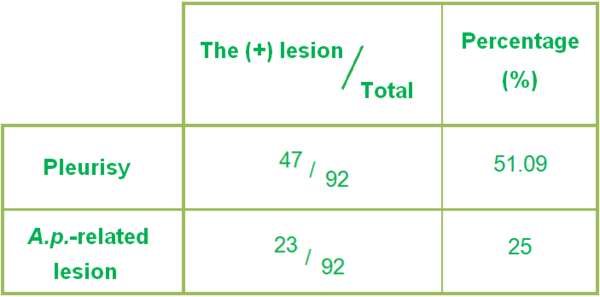
Table 2 Results of lung scoring at the slaughterhouse
The result in Table 2 showed that the A.p.–related pleurisy ratio is 25%. The APPI index of this batch is also high (APPI = 0.85).
In general, A.p. is in chronical form in this selected farm. However, this bacterium influences the performance of the farm. That’s why it’s necessary to apply the reasonable controllable measures to improve the performance of the farm. In particular, it needs to compare the efficacy between the vaccination and the antibiotic.
^ Top page
.
GROUPING IN THE TRIAL
The weaned pigs are devided into 3 groups:
- Group 1 (Vaccine): 240 piglets, is vaccinated with a toxoid vaccine, Coglapix@, at 8 and 12 weeks of age.
- Group 2 (Antibiotic): 240 piglets, receives an specific antibiotic program, Tilmicosin (200ppm), in the diet within 3 weeks, at 6 weeks and 3 months of age.
- Group 3 (Control): 40 piglets, receive neither vaccine nor specific antibitotic.
All 3 groups are raised in the same house with the common feed at Vietnam (feed is mixed with CTC (400ppm) and Colistin (100ppm)).
Image 5 Farm in the trial
^ Top page
.
RESULT
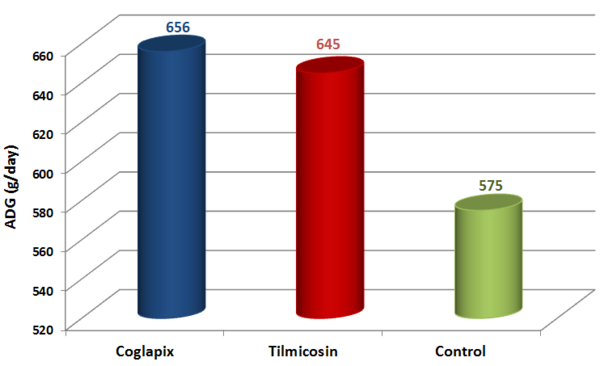
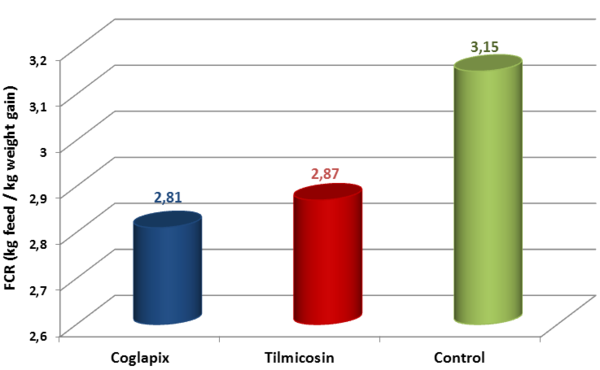
The performance of the Vaccine and Antibiotic group are similar. Moreover, the ADG of these 2 groups is higher and the FCR is lower than the Control group (Figure 1 & 2).
Figure 1 Average Daily Gain from 56 to 183 days of age
Figure 2 Feed Conversion Ratio from 56 to 183 days of age
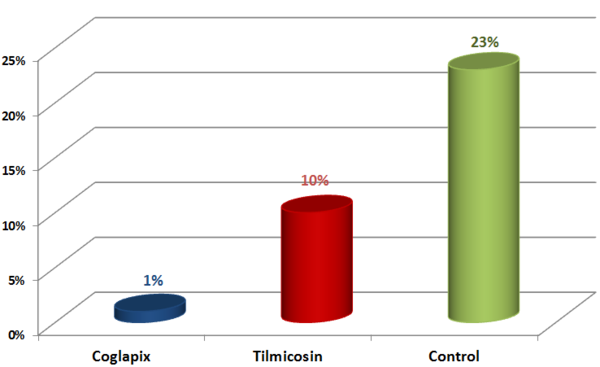
The results of the lung scoring at the slaughter house showed that the A.p.-related lesions of the Vaccine group has been significantly reduced versus the Antibiotic and Control group (Figure 3).
Figure 3 The A.p.–related pleurisy ratio
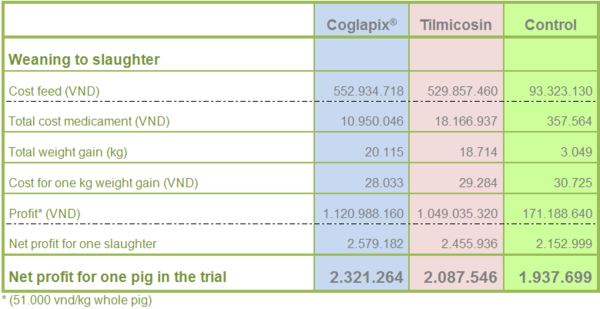
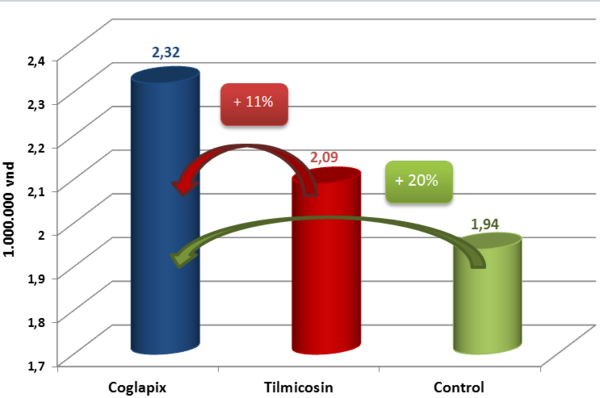
As the economic impact, the Vaccine group gains 2.321.264 VND of profit in each fattening pig, like as the Table 3.
Table 3 The cost and profit in each group
Therefore the group that applies the vaccination with Coglapix®, has the profit of 11% more than the group use the Tilmicosin and of 20% more than the Control group (Figure 4).
Figure 4 Average profit in each pig
^ Top page
.
CONCLUSION
The Vaccine group (with Coglapix®) and Antibiotic group have the higher performance and more profit than the Control group. Although the similar performance, the economic impact given by the Vaccine group is more improved than the Antibiotic group. Today, in the effort to reduce the use of antibiotic in feed, the vaccination shows that this measure is an efficient solution to control A.p.
^ Top page
.

 Corporate Website
Corporate Website
 Africa
Africa
 Argentina
Argentina
 Asia
Asia
 Australia
Australia
 Belgium
Belgium
 Brazil
Brazil
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile
Chile
 China
China
 Colombia
Colombia
 Denmark
Denmark
 Egypt
Egypt
 France
France
 Germany
Germany
 Greece
Greece
 Hungary
Hungary
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Italia
Italia
 India
India
 Japan
Japan
 Korea
Korea
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Mexico
Mexico
 Middle East
Middle East
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Peru
Peru
 Philippines
Philippines
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Romania
Romania
 Russia
Russia
 South Africa
South Africa
 Spain
Spain
 Sweden
Sweden
 Thailand
Thailand
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
 Ukraine
Ukraine
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 USA
USA
 Vietnam
Vietnam