...
--> Unfertilized / fertilized egg
--> Day 1
--> Day 2
--> Day 3
--> Day 4
--> Day 5
--> Day 6
--> Day 7
--> Day 8
--> Day 9
--> Day 10
--> Day 11
--> Day 12
--> Day 13
--> Day 14
--> Day 15 & 16
--> Day 17
--> Day 18
--> Day 19
--> Day 20
--> Day 21
...
EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT, DAY BY DAY
By Dr Stephan WARIN, DVM, Avian Business Unit.
CEVA Santé Animale, La Ballastiere, BP 126, 33501 Libourne Cedex, France
.
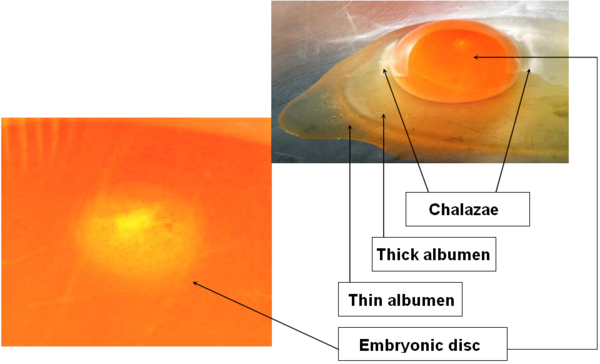
UNFERTILIZED / FERTILIZED EGG
Unfertilized egg: The embryonic disc of a sterile egg bears an accumulation of white material at its center.
Image 1 Unfertilized
Fertilized egg: The fertilized embryonic disc looks like a ring: it has a central area, lighter in color, which is to house the embryo.
.
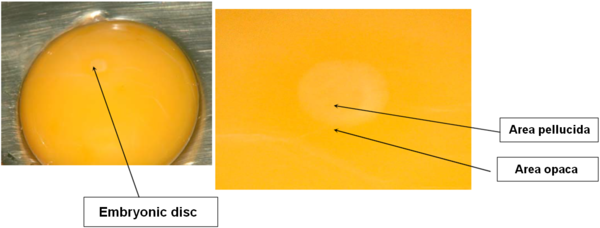
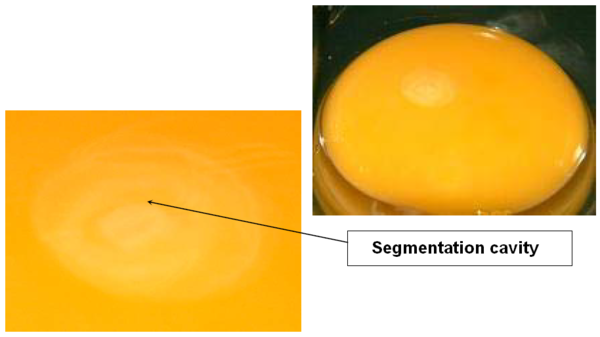
DAY 1
The germinal disc is at the blastodermal stage.
The segmentation cavity, under the area pellucida, takes on the shape of a dark ring.
Image 3 Embryonic development, day 1
.
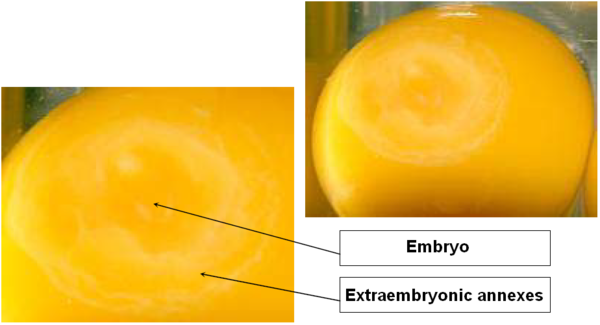
DAY 2
Appearance of the first groove at the center of the blastoderm.
Among extraembryonic annexes, appearance of the vitelline membrane which is going to play a major role in embryo nutrition.
Image 4 Embryonic development, day 2
.
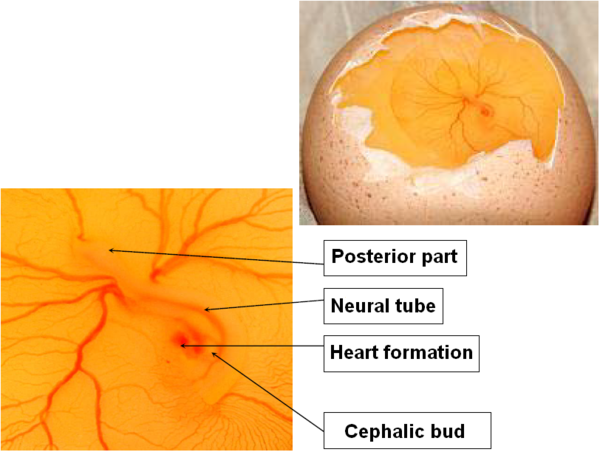
DAY 3
The embryo is lying on its left side.
Onset of blood circulation.
The vitelline membrane spreads over the yolk surface.
The head and trunk can be discerned, as well as the brain.
Appearance of the cardiac structures which begin to beat.
Image 5 Embryonic development, day 3
.
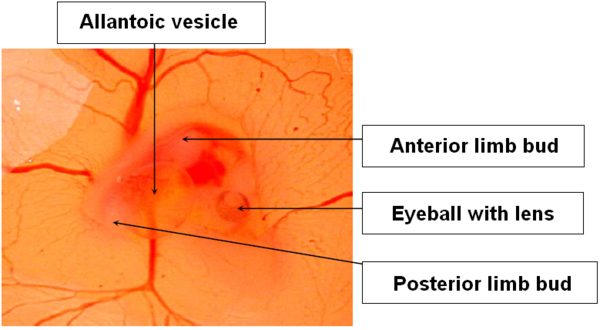
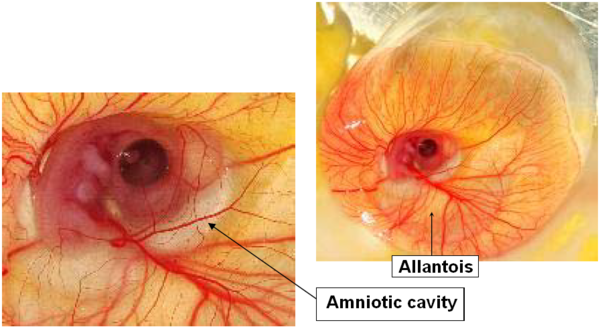
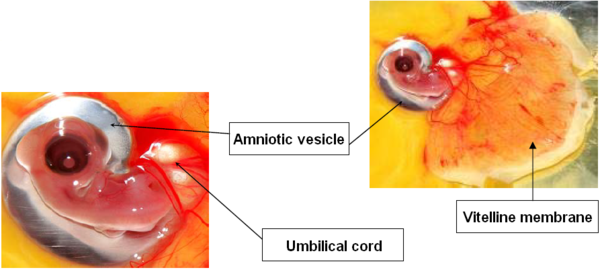
DAY 4
Development of the amniotic cavity, which will surround the embryo: filled with amniotic fluid, it protects the embryo and allows it to move.
Appearance of the allantoic vesicle: it plays a major role in calcium resorption, respiration and waste storage.
Image 6 Embryonic development, day 4
.
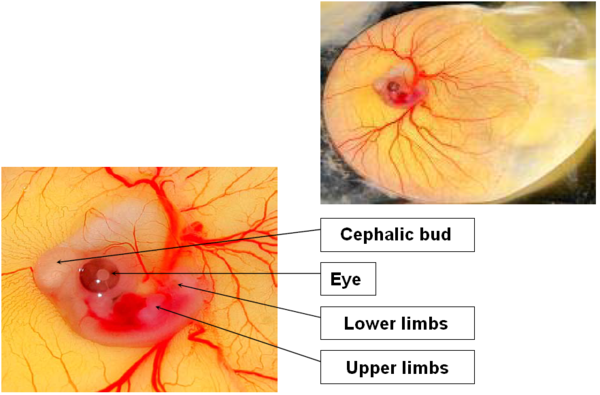
DAY 5
Sensible increase in the embryo’s size; the embryo takes a C shape: the head moves closer to the tail.
Extension of limbs. Differentiation of the fingers of the inferior limbs.
Image 7 Embryonic development, day 5
.
DAY 6
The vitelline membrane continues to grow and now surrounds more than half the yolk.
Fissura between the first, second and third fingers of the upper limbs, and between the second and third fingers of the lower limbs.
The second finger is longer than the others.
Image 8 Embryonic development, day 6
.
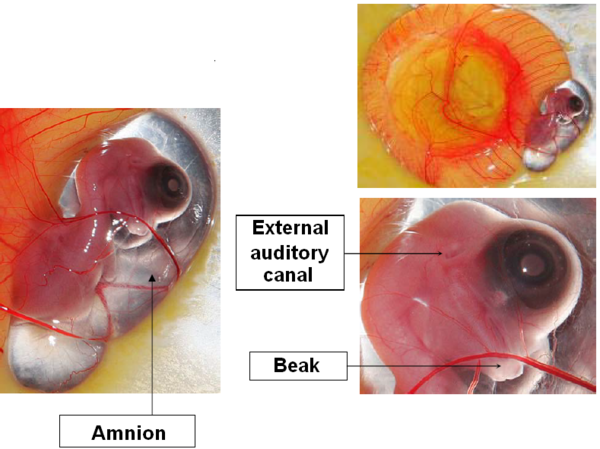
DAY 7
Thinning of the neck which now clearly separates the head from the body.
Formation of the beak.
The brain progressively enters the cephalic region: it progressively grows smaller proportionally to the embryo’s size.
Image 9 Embryonic development, day 7
.
DAY 8
The vitelline membrane covers almost the whole yolk.
Eye pigmentation is readily visible.
The beak’s upper and lower parts are differentiated, as well as the wings and legs.
The neck stretches.
The brain is completely settled in its cavity.
Opening of the external auditory canal.
Image 10 Embryonic development, day 8
.
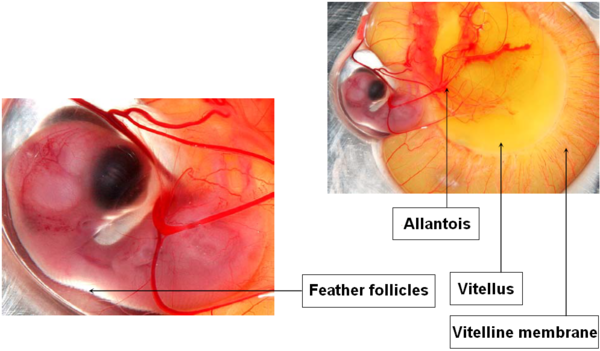
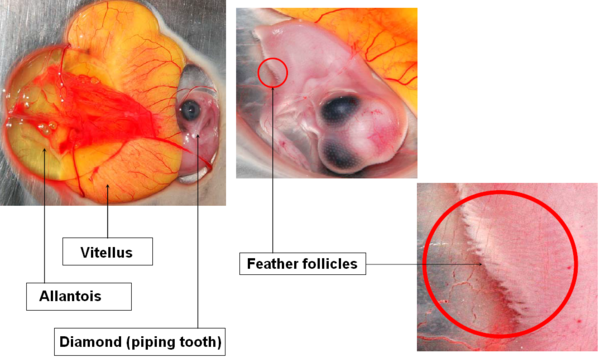
DAY 9
Appearance of claws.
Budding of the first feather follicles.
Growth of the allantois and increased vascularization of the vitellus.
Image 11 Embryonic development, day 9
.
DAY 10
The nostrils are present as narrow apertures.
Growth of eyelids.
Extension of the distal portion of the limbs.
The vitelline membrane completely surrounds the yolk.
Feather follicles now cover the inferior part of the limbs.
Appearance of the egg-tooth.
Image 12 Embryonic development, day 10
.
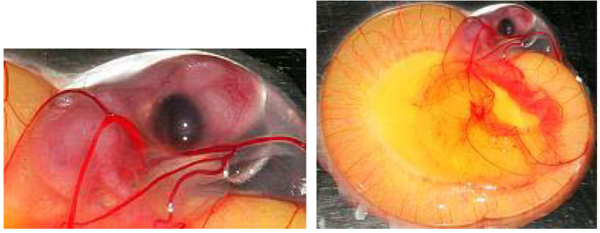
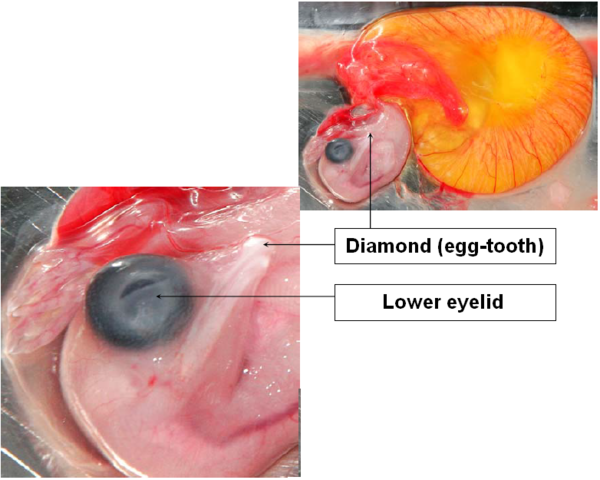
DAY 11
The palpebral aperture has an elliptic shape that tends to become thinner.
The allantois reaches its maximum size while the vitellus begins to shrink.
The embryo now has the aspect of a chick.
Image 13 Embryonic development, day 11
.
DAY 12
Feather follicles surround the external auditory meatus and cover the upper eyelid.
The lower eyelid covers two thirds, or even three quarters, of the cornea.
Image 14 Embryonic development, day 12
.
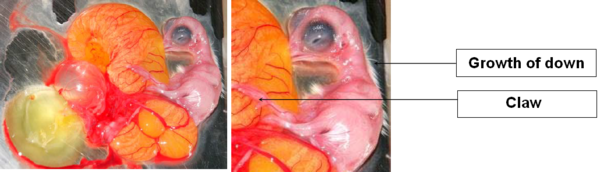
DAY 13
The allantois shrinks to become the membrane.
Appearance of claws and leg scales.
Image 15 Embryonic development, day 13
.
DAY 14
Down covers almost the whole body and grows rapidly.
Image 16 Embryonic development, day 14
.
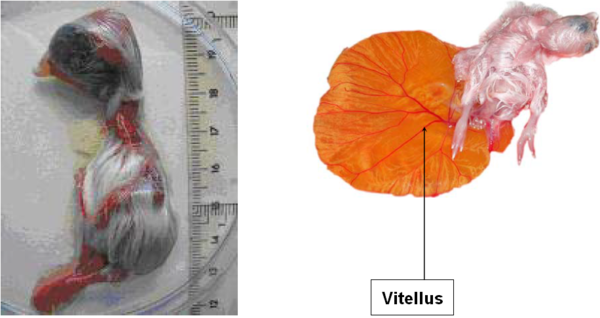
DAY 15 & 16
Few morphological changes: chick and down continue to grow.
Vitellus shrinking accelerates.
Progressive disappearance of the egg white.
The head moves toward pipping position, under the right wing.
Image 17 Embryonic development, day 15 & day 16
.
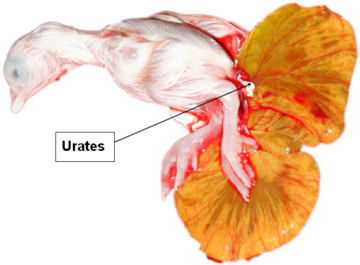
DAY 17
The embryo’s renal system produces urates.
The beak, which is under the right wing, points to the air cell.
The egg white is fully resorbed.
Image 18 Embryonic development, day 17
.
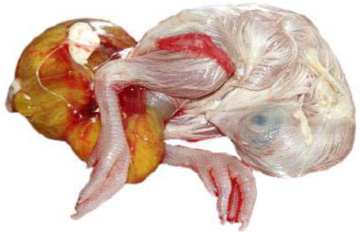
DAY 18
Onset of vitellus internalization.
Reduction in the amount of amniotic fluid.
This is the time for transfer from incubator to hatcher, and also perhaps in ovo vaccination.
Image 19 Embryonic development, day 18
.
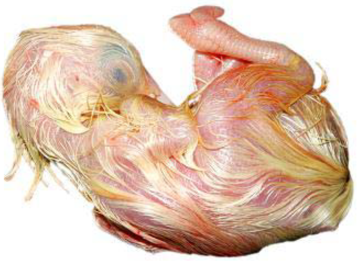
DAY 19
Acceleration of vitellus resorption.
The beak is against the inner shell membrane, ready to pierce it.
Image 20 Embryonic development, day 19
.
DAY 20
Vitellus fully resorbed; closing of the umbilicus.
The chick pierces the inner shell membrane and breathes in the air cell.
Gas exchanges occur through the shell, which is porous.
The chick is ready to hatch. Piercing of the shell begins.
Image 21 Embryonic development, day 20
.
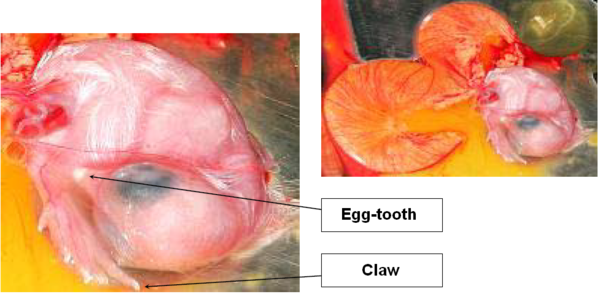
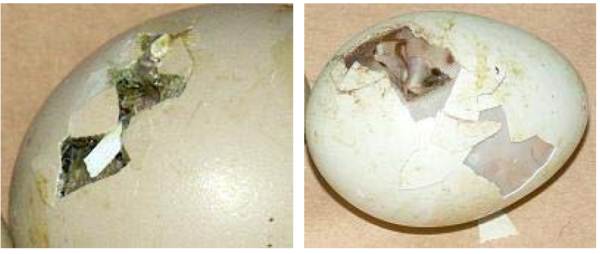
DAY 21
The chick uses its wing as a guide and its legs to turn around and pierce the shell in a circular way by means of its egg-tooth.
Image 22 Egg at hatching, day 21
It extricates itself from the shell in 12 to 18 hours and lets its down dry off.
If you need to download this article, please do not hesitate to contact us!

 Corporate Website
Corporate Website
 Africa
Africa
 Argentina
Argentina
 Asia
Asia
 Australia
Australia
 Belgium
Belgium
 Brazil
Brazil
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile
Chile
 China
China
 Colombia
Colombia
 Denmark
Denmark
 Egypt
Egypt
 France
France
 Germany
Germany
 Greece
Greece
 Hungary
Hungary
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Italia
Italia
 India
India
 Japan
Japan
 Korea
Korea
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Mexico
Mexico
 Middle East
Middle East
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Peru
Peru
 Philippines
Philippines
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Romania
Romania
 Russia
Russia
 South Africa
South Africa
 Spain
Spain
 Sweden
Sweden
 Thailand
Thailand
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
 Ukraine
Ukraine
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 USA
USA
 Vietnam
Vietnam